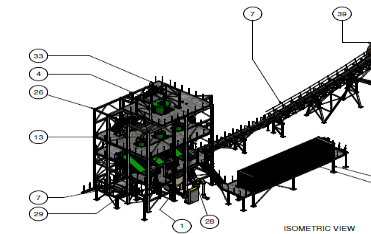
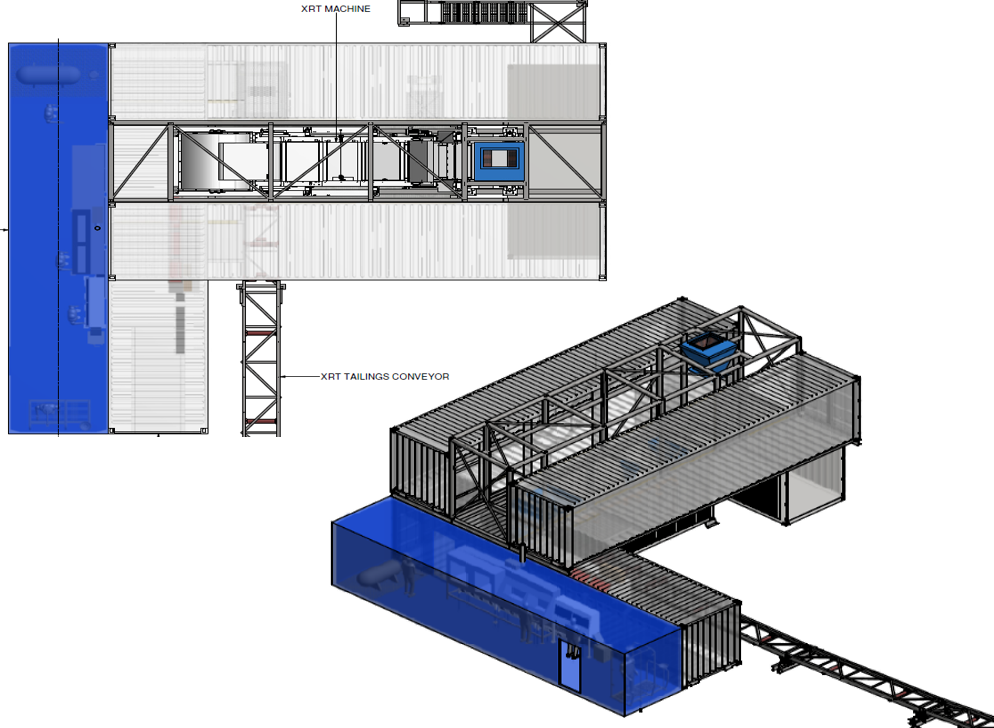
Factors Which Lead to Success
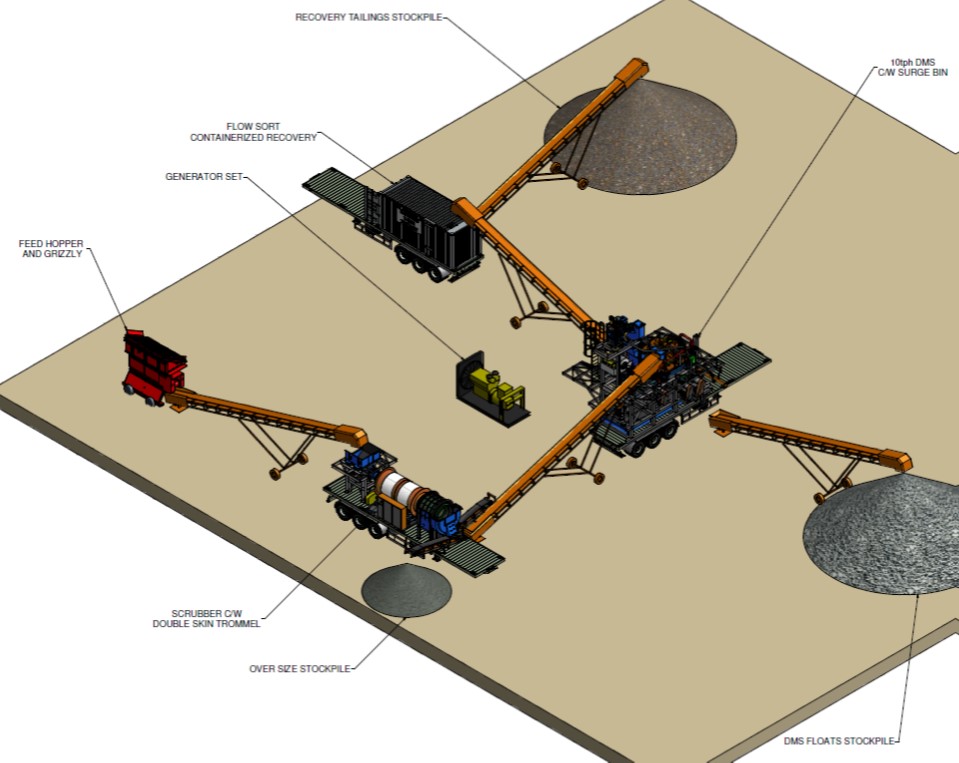
1st Stage: Front End Ore Preparation
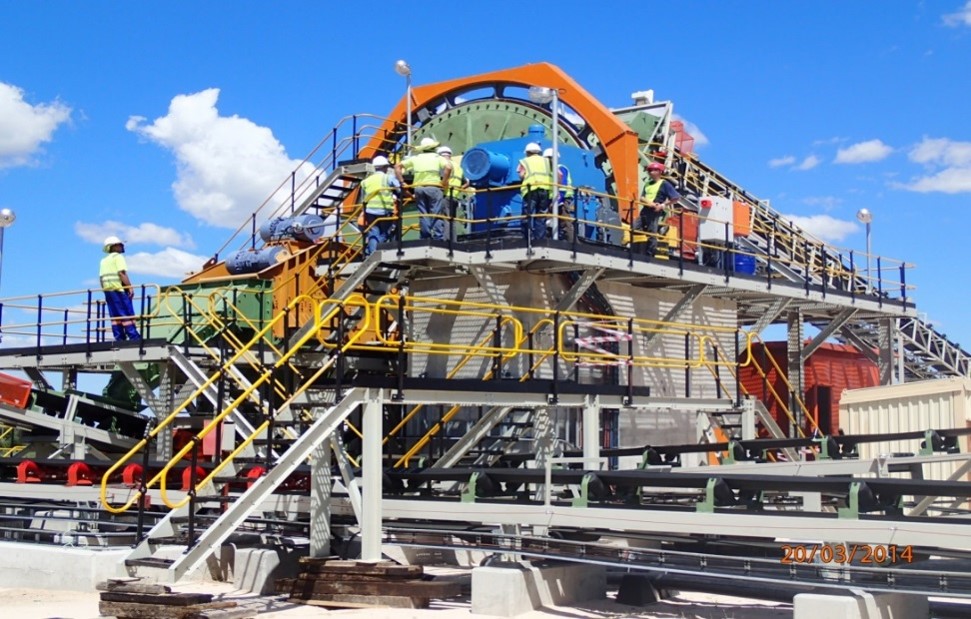
2nd Stage: Crushing and Processing
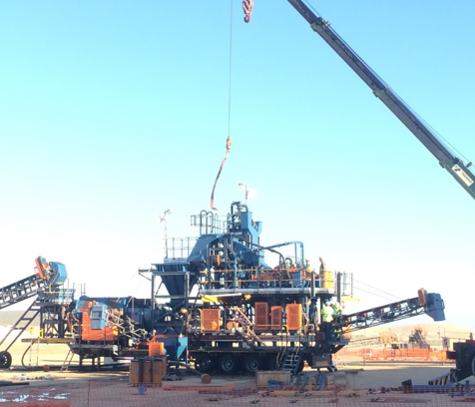
3rd Stage: Enhanced Diamond Recovery
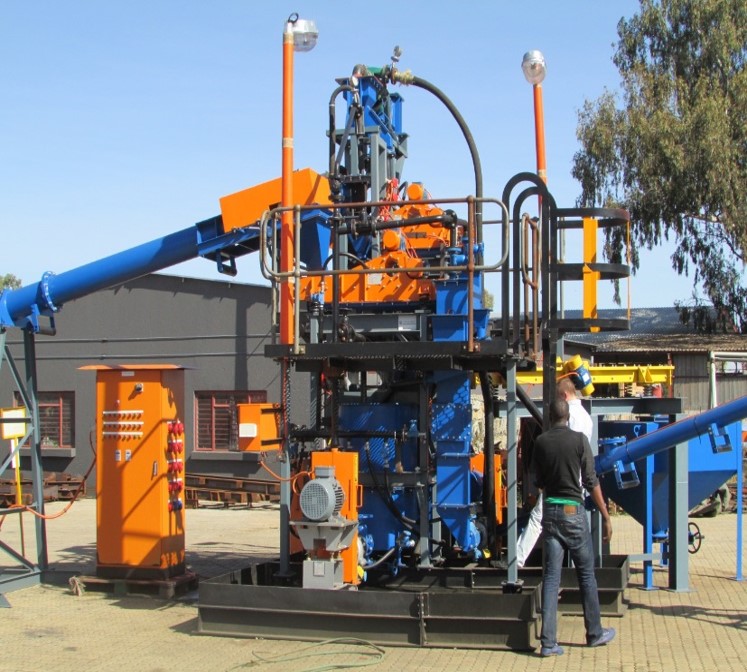


1. DMS only no pre-concentration |
2. Front-end: screening and scrubbing |
3. Mobile-wheel or skid mounted |
4. Capital: R10 million to R20 million |

Crushing and screening – re-circulating load |
Jet pumps from DMS to final recovery. XRT Large stones |
XRT reduces DMS capacity |
Capex: R350-R400 million |